Which Underwater Cable is Right for You? Waterproof, Water-Resistant, or Watertight?
When it comes to selecting the best underwater cable, there are three main categories to consider: waterproof, water-resistant, and watertight cables. Each type is designed for a different level of moisture exposure, and understanding the differences can make a huge difference in performance, durability, and safety.
Whether you're working in a damp environment or need cables that can withstand full submersion, this guide will help you navigate the most important features and uses of each type.
Understanding the Differences: Waterproof, Water-Resistant, and Watertight
While these terms may seem interchangeable, each represents a distinct level of moisture protection:
Water-Resistant: Offers some protection against water but isn't fully waterproof. Suitable for applications with occasional splashes or damp conditions.
Waterproof: Completely prevents water from entering, ideal for environments with high moisture exposure but not high pressure.
Watertight: Prevents water ingress even under pressure, making it ideal for full submersion, especially in applications with variable depths and pressures.
In summary:
| Type |
Protection Level |
Common Applications |
| Water-Resistant |
Protection from splashes and dampness |
Indoor industrial spaces, minor exposure |
| Waterproof |
Full protection against water but not high pressure |
Outdoor environments, rain, wash-down areas |
| Watertight |
Full protection against water under pressure |
Submerged environments, underwater installations |
Components of a Reliable Underwater Cable System
The quality and waterproofing of cable connections—the points where cables, connectors, and plugs meet—play a crucial role in performance. The following components each contribute to a secure and water-resistant system:
Cable Insulation: The main defense against water, often made of waterproof materials like PVC, polyurethane, or rubber.
Connectors and Glands: Designed to keep out moisture, these points of connection must match or exceed the cable’s water-resistance rating.
Plug Connectors: In harsh, wet environments, these should be both waterproof and watertight to prevent dangerous short circuits.
These elements ensure a continuous flow of power or data without interruptions, even in moist or submerged conditions.
Applications: When to Use Water-Resistant, Waterproof, and Watertight Cables
Let’s look at specific applications where these cables excel and what protection they offer.
| Cable Type |
Typical Applications |
Key Benefits |
| Water-Resistant |
Food processing, damp industrial spaces |
Resists splashes, affordable |
| Waterproof |
Outdoor use, marine, and boating |
Fully waterproof for rain and spray protection |
| Watertight |
Underwater exploration, offshore oil rigs |
Protection in high-pressure, submerged environments |
Food Industry: High standards of hygiene require equipment to withstand steam and water for cleaning. Waterproof cables ensure safety in wet areas without constant maintenance.
Marine and Outdoor Installations: Waterproof cables are essential for offshore platforms, boats, and outdoor equipment, providing reliable performance in environments with high salt and humidity levels.
Submersible and Deep-Sea Exploration: For high-pressure underwater environments, watertight cables are a necessity, preventing water ingress under the extreme pressure found in deeper water applications.
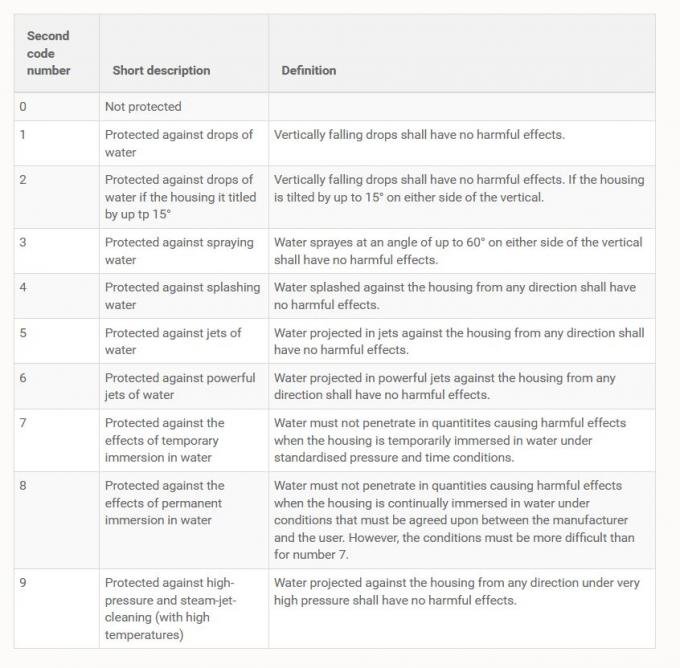
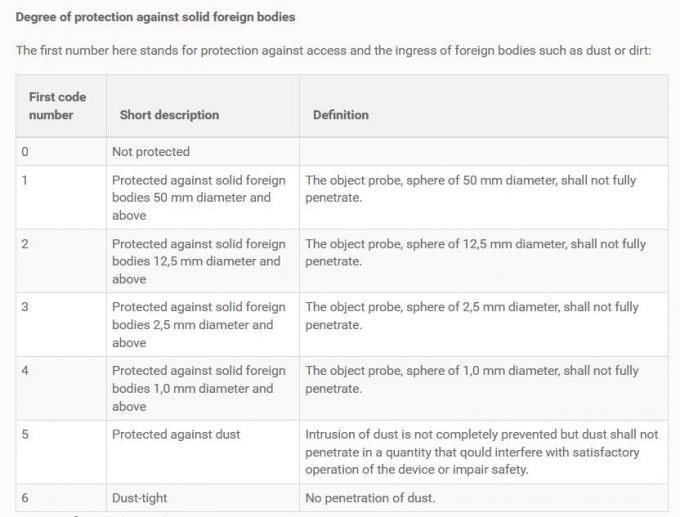
IP Ratings: How to Choose Based on Water Protection Levels
The IP rating system is a standardized way to determine a product’s protection against water and dust. The second number in the IP code (IPXX) indicates its level of water protection:
| IP Rating |
Water Protection Level |
Ideal For |
| IPX0 |
No protection |
Indoor, dry environments |
| IPX4 |
Protection from splashes |
Indoor/outdoor damp spaces |
| IPX7 |
Immersion in water up to 1 meter |
Temporary underwater use |
| IPX8 |
Full submersion, typically at specific depths |
Continuous underwater use |
| IPX9 |
High-pressure, high-temperature jets |
Industrial cleaning processes |
Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Cable
When selecting an underwater cable, it’s essential to assess your specific environment:
Exposure Level: Consider whether the cable will be exposed to splashes, full submersion, or high-pressure jets.
Pressure: For applications that involve depth, watertight cables designed to withstand high pressures are necessary.
Temperature: Extreme temperatures can impact cable performance, so check for heat resistance if necessary.
Chemical Compatibility: In environments exposed to chemicals (such as salt in seawater or industrial solvents), select cables with specific chemical resistance.
Longitudinal vs. Lateral Waterproofing
Waterproof cables can offer two distinct types of water protection:
Lateral Waterproofing: Prevents water from entering the cable sheath.
Longitudinal Waterproofing: Stops water from traveling along the cable, especially important if one end becomes submerged.
| Waterproofing Type |
Description |
Suitable For |
| Lateral |
Prevents water entry into the sheath |
General wet environments |
| Longitudinal |
Stops water from moving within cable |
Submerged applications |
These properties are especially important in underwater applications where cables are fully or partially submerged.
Material Considerations for Underwater Cables
The materials used in waterproof and water-resistant cables vary significantly, impacting durability, flexibility, and resilience against harsh environments:
Polyurethane (PU): Highly resistant to abrasion and water. Ideal for outdoor use.
Rubber (Neoprene): Offers excellent flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring movement.
PVC: Versatile and affordable, suitable for light-duty water-resistant needs but less robust than PU or rubber in fully submerged conditions.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs
When selecting the right underwater cable for your application, it is essential to consider the level of moisture exposure and any additional environmental factors. Here’s a summary to help you decide:
| Application |
Recommended Cable Type |
IP Rating |
| Minor splashes |
Water-resistant |
IPX4 |
| Regular rain/spray |
Waterproof |
IPX7 |
| Submersion |
Watertight |
IPX8 or IPX9 (pressure) |
Understanding the subtle differences in water protection levels, from water-resistant to watertight, and selecting the right IP-rated cable for your unique environment can save time, cost, and potentially prevent dangerous electrical failures.
A well-chosen underwater cable ensures your operations run smoothly and safely, no matter how damp or submerged the conditions may be.

