
What is the AS/NZS 2802:2000 Standard and What is the Difference Between AS/NZS 1802:2003 ?
The AS/NZS 2802:2000 and AS/NZS 1802:2003 standards are both Australian/New Zealand standards that pertain to electric cables used in mining and other similar industries. However, they cover different types of cables with specific characteristics.
While both AS/NZS 2802:2000 and AS/NZS 1802:2003 set standards for reeling and trailing cables in mining, their scopes differ significantly due to the specific environmental and safety requirements of their respective applications.
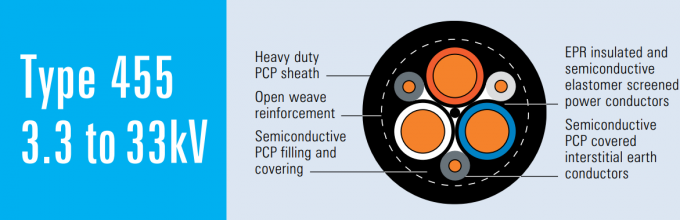
AS/NZS 2802:2000 is broader and applies to general mining and industrial uses, whereas AS/NZS 1802:2003 is tailored to the unique and hazardous conditions of underground coal mining. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate cables for specific mining operations.
Australia_&_New_Zealand_Standards_Feichun_Mining_Cable.pdf
Title: Electric Cables - Reeling and Trailing - For Mining and General Use (Other Than Reeling)
Scope: This standard specifies the requirements for flexible electric cables designed for use in mining and general industrial applications, particularly for reeling and trailing purposes. These cables are often subjected to rough conditions, including mechanical stress, exposure to harsh environments, and frequent handling. The standard addresses aspects such as construction, dimensions, electrical performance, mechanical properties, and testing methods to ensure that the cables are suitable for their intended use.
Applications: Primarily used in mining, tunneling, and other industrial operations where cables need to be robust and flexible enough to withstand continuous movement and harsh conditions.

Application Focus:
AS/NZS 2802:2000:
Primarily covers reeling and trailing cables for mining and other general uses, with a broader scope including non-reeling applications.
AS/NZS 1802:2003:
Focuses specifically on reeling and trailing cables used in mining, particularly in harsh and rugged environments.

Cable Types:
AS/NZS 2802:2000: Includes cables used for reeling, trailing, and other general purposes.
AS/NZS 1802:2003: Targets cables specifically designed for trailing in mining environments.
Technical Specifications:
There may be variations in the technical specifications, such as the construction requirements, insulation, sheath materials, and mechanical strength, due to the different intended applications of the cables in each standard.
These standards ensure that the cables used in mining and industrial settings are safe, reliable, and capable of withstanding the harsh conditions they are exposed to.
Differences in technical specifications:
Structural design:
The cable design in AS/NZS 2802:2000 needs to meet the needs of a wider range of industrial applications, and may need to be designed to take into account different occasions, such as being suitable for both coiled and non-coiled uses.
The cables in AS/NZS 1802:2003 focus on traction applications in mines, and the design pays more attention to special requirements such as abrasion resistance, pressure resistance and moisture resistance.
Insulation and sheathing materials:
Polymer materials and manufacturing processes
To fully comply with these two standards, strict requirements are placed on the cable's polymer materials and manufacturing process.
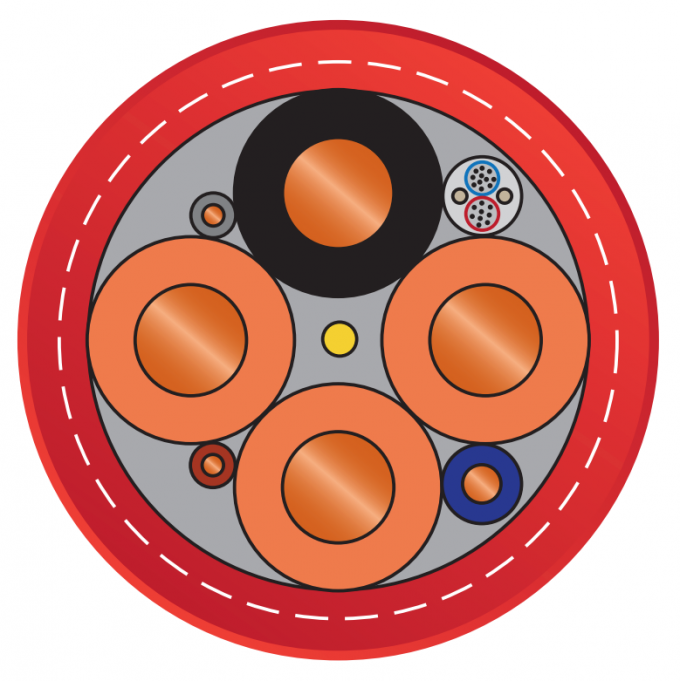
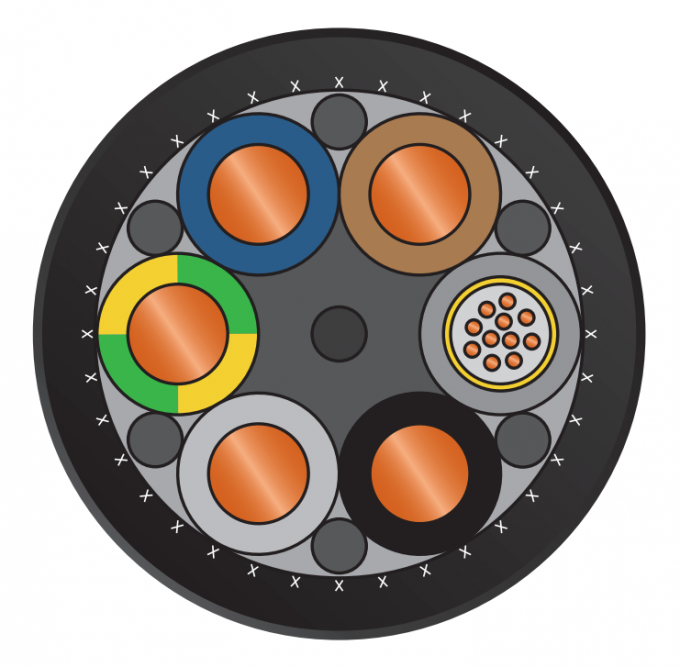
Insulating material:
Sheath material:
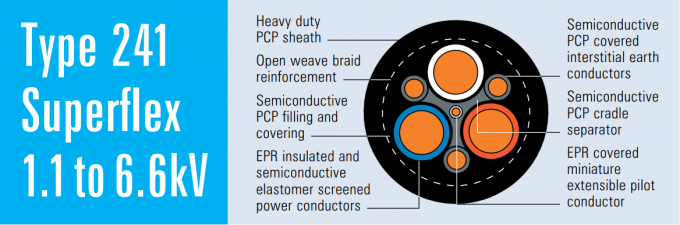

Manufacturing process

Although both AS/NZS 2802:2000 and AS/NZS 1802:2003 are standards for cables for mining and industrial purposes, they have different application scenarios and technical requirements.
Full compliance with these standards requires the selection of appropriate polymer materials and the use of precision manufacturing processes to ensure that the cables can operate safely and reliably in harsh environments.
