Reeling Cable ( DIN VDE Standard ) Model Naming Rules
When it comes to choosing the right reeling cable for your specific application, understanding the model naming rules can be a game-changer.
For professionals working with electrical equipment in industrial settings, the naming conventions set by DIN VDE standards play a critical role in identifying the right cable for the job.
The combination of letters and numbers may look complex at first glance, but it’s actually a well-structured code that gives detailed information about the cable’s construction, usage, and specifications.
In this guide, we’ll break down the naming rules for reeling cables under the DIN VDE standard to help you better understand what each letter and number means.
This way, you’ll be able to quickly identify the right cable for your needs, whether you are working in heavy-duty applications, mobile equipment, or industrial cranes.
Why Understanding DIN VDE Naming Rules Matters ?
The DIN VDE standard is an important guideline in the electrical industry, especially when it comes to cables. These codes help engineers and installers to easily distinguish between different types of cables.
Whether you're working with tough rubber-sheathed flexible reeling cables or polyurethane-sheathed cables for specific uses, knowing the meaning of the letters and numbers will ensure you pick the correct type, ensuring both safety and performance.
For instance, reeling cables are often used in harsh environments, so selecting the wrong type could lead to premature wear or even failure, potentially endangering your equipment and personnel.
Choosing the right cable ensures durability, safety, and compliance with industry standards.
Breaking Down the Naming Rules
The type designation for a cable is a combination of letters and numbers, each representing a specific characteristic.
Here's what these codes mean for different types of reeling cables according to the DIN VDE standard:
Common Cable Models and Their Meanings
(N)SHTÖU: This is a tough rubber-sheathed flexible reeling cable used in demanding environments. The "N" stands for its design according to the corresponding standard, while "SHT" indicates that it's a 1 kV reeling cable. The "ÖU" suffix means that the cable is oil-resistant and has a flame-retardant outer sheath.
(N)7YRDGÖU: This represents an EVA sheathed cable for spring-reeling applications. The EVA material gives it higher flexibility and durability. "ÖU" means it's oil-resistant and flame-retardant, just like the SHTÖU model.
D12Y11YU11Y: This type is a polyurethane-sheathed reeling cable. Polyurethane offers excellent abrasion resistance, which makes it suitable for applications involving high mechanical stress. The "Y" indicates that the cable has a PVC compound, while the "11Y" refers to the PUR compound used in its construction.
(N)GRDGÖU: A round rubber-sheathed flexible festoon cable, which is often used for simple reeling. "ÖU" indicates that it has an oil-resistant, flame-retardant outer sheath, making it ideal for tough environments. The "R" signifies that the cable is round in shape, and "G" stands for rubber compound.
Key Components of the Model Naming Rules
C: This letter in a cable's name indicates the presence of a conducting metal casing over the stranded cores or between the inner and outer sheath, which serves as a shield.
CE: When you see this in the code, it means there’s a conducting metal casing over the insulation of the outer conductors, providing extra protection and shielding.
CG: This indicates a conducting non-metal casing over the stranded cores or between the inner and outer sheath. It is an alternative to the metal shield and is commonly used for lightweight applications.
D: Refers to internal specifications based on the manufacturer’s design, which can sometimes be customized for specific applications.
FL: This indicates a flat cable, which is often used in environments where space is limited.
FO: Refers to fiber-optic cables within the reeling cable, commonly used for data transmission in addition to power supply.
G: This letter stands for rubber compound, which is frequently used for the outer sheath of cables to ensure flexibility and durability.
HS: Denotes high-voltage (HV) capabilities, meaning the cable is designed to handle higher voltages for heavy-duty applications.
J: This letter means the cable includes a green/yellow-marked core, usually for protective grounding purposes.
T: Refers to a support element within the cable, often used to ensure the cable remains stable and durable during operation.
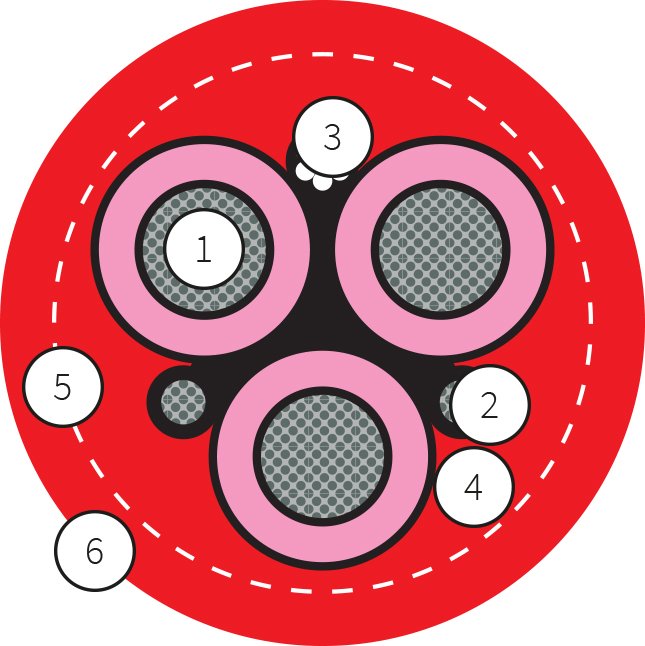
Examples of Cable Designations
(N)SHTÖU: As discussed, this is a tough, flexible reeling cable with a flame-retardant outer sheath, suitable for environments where mechanical stress and oil-resistance are crucial.
(N)TSKCGEWÖU: A medium-voltage reeling cable with a cradle separator. The cradle separator allows the cable to handle higher mechanical stress during operation, such as in mining or crane applications. The "ÖU" ensures it's suitable for oil-exposed environments.
D12YST11YU11Y: This polyurethane-sheathed reeling cable is specially designed for vertical applications, such as those involving spreader reels. The "Y" stands for PVC compound and "11Y" for PUR compound, making it resistant to abrasion and harsh conditions.
(N)TSCGEWÖU: This is a round medium-voltage reeling cable, capable of handling voltages from 6 to 20 kV. The presence of "CGE" indicates that the cable has non-metal shielding for the outer conductors, ensuring safety in heavy-duty applications like mining and industrial operations.
Why Model Naming Rules Are Important for Your Business
For companies dealing with industrial machinery, cranes, or mining operations, choosing the right cable is essential to ensure operational efficiency and safety.
By understanding the DIN VDE naming conventions, you can:
Quickly identify the correct cable type for specific applications.
Ensure that the cable meets the required voltage and mechanical stress levels.
Select cables with the right sheath materials for oil resistance, flame retardance, or UV protection.
By choosing cables that meet your operational needs, you minimize downtime, reduce the risk of cable failure, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Choosing the right reeling cable for your industrial application is vital for ensuring both performance and safety.
The DIN VDE standard provides a clear set of naming rules that allow you to easily identify the cable’s specifications, from voltage rating to sheathing materials.
Understanding these naming conventions not only helps you make better purchasing decisions but also ensures that you comply with safety standards in harsh environments like mining, ports, and heavy industrial operations.
Always look for key indicators like SHT, G, ÖU, and FL to know exactly what type of cable you're working with.
Investing in the right cable today can prevent costly equipment failures and keep your operations running smoothly, even in the most demanding conditions.
Make sure to choose your reeling cable carefully and understand the importance of every letter and number in its name!





