
When working with cables in environments exposed to water, selecting the right waterproof cable is critical to ensuring uninterrupted service and long-term reliability. The choice often comes down to two main types: laterally waterproof cables and longitudinally waterproof cables.
But what sets these two apart, and how do you know which type is best for your application? Let's dive into the core differences, mechanisms, applications, and importance of each cable type to help you make the most informed choice.
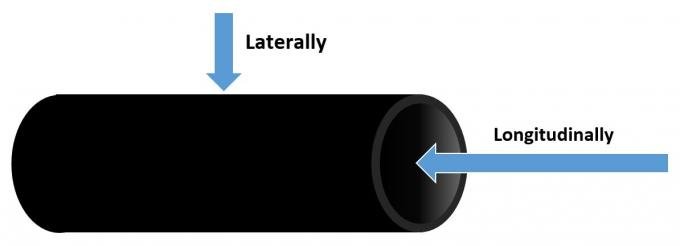
Water ingress is a serious issue in cable technology. It can lead to short circuits, signal degradation, and in severe cases, complete system failure.
Waterproof cables are specially designed to combat these risks, but how they achieve this depends on whether they use lateral or longitudinal waterproofing.
| Cable Type | Protection Mechanism | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Laterally Waterproof Cable | Prevents water from entering through the sides | Outdoor installations, underground setups |
| Longitudinally Waterproof Cable | Prevents water from spreading along the cable length | Connections, joint areas, high-risk zones |
Laterally waterproof cables are constructed to stop water from seeping in from the sides. This is especially useful in underground installations or outdoor settings, where side water ingress is common due to environmental exposure.
In these cases, the outer layer or sheath acts as a robust barrier, stopping moisture in its tracks.
The lateral waterproofing in these cables is typically achieved through layers of protective materials like aluminum/polyester tape. This tape is bonded to the underside of the outer sheath, creating a seamless barrier against side water ingress.
As a result, these cables excel in areas where water exposure comes mainly from the sides rather than through the ends or connections.
Key Feature: Lateral waterproofing guards against side moisture, perfect for underground or outdoor applications.
Common Use Cases: Used in settings such as tunnels, railways, and telecommunication systems where side exposure to water is a common concern.
Longitudinally waterproof cables work differently. Instead of protecting against side water ingress, they prevent water from traveling along the length of the cable.
This feature is vital in situations where water might enter at a connector or damaged section and then spread down the cable, potentially causing widespread issues.
Longitudinal waterproofing typically involves water-blocking tapes or water-swellable powders. These materials swell upon contact with water, blocking its movement and confining the moisture to a limited area.
By doing so, they prevent any damage from spreading along the cable, making them ideal for high-risk zones like connection points.
Key Feature: Longitudinal waterproofing restricts moisture spread along the length of the cable.
Common Use Cases: Common in power lines, outdoor junctions, and telecommunication cables exposed to potential water ingress from connections.
To understand the best applications for each type, it’s essential to compare their key features and ideal use cases side-by-side.
| Feature | Laterally Waterproof Cables | Longitudinally Waterproof Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Protection Direction | Side water ingress | Water spread along cable length |
| Typical Barrier Material | Aluminum/polyester tape | Water-swellable tapes or powders |
| Ideal Applications | Outdoor environments, tunnels, railways | Junction points, areas prone to damage |
| Primary Risk Mitigation | Side moisture, environmental exposure | Entry-point moisture spread prevention |
In sectors such as telecommunications, power distribution, and industrial settings, cables are often exposed to wet or damp environments.
By preventing water ingress, these waterproof cables offer enhanced reliability and reduce downtime.
When cables are installed in trenches, conduits, or along ground surfaces, laterally waterproof cables excel due to their robust side barriers.
They are less vulnerable to direct water exposure along the length, making them reliable in outdoor installations where side water seepage is the primary risk.
In applications where water entry may occur at specific points, such as connectors or potential damage sites, longitudinally waterproof cables are the ideal choice.
These cables prevent the spread of water along their length, crucial for telecommunication systems and power networks where one breach can have a widespread impact.
When choosing the right cable for your project, consider factors like environmental conditions, installation settings, and type of water exposure.
Here’s a guide to help you decide based on common application needs.
| Environmental Condition | Recommended Waterproof Cable Type | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Consistent Moisture from All Sides | Laterally Waterproof Cable | Ideal for outdoor and underground installations |
| Risk of Water Entry at Specific Points | Longitudinally Waterproof Cable | Best for connection points or damaged sections |
| High Environmental Humidity | Laterally Waterproof Cable | Protective side layers help prevent seepage |
| Potential Connector Water Exposure | Longitudinally Waterproof Cable | Prevents water spread along cable length |

Understanding the advantages and limitations of each type can help guide your decision, ensuring that your cable choice offers optimal protection and performance.
| Feature | Laterally Waterproof | Longitudinally Waterproof |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent for side moisture | Effective for point-entry water resistance |
| Flexibility in Harsh Environments | High durability in side-exposed areas | Strong performance at connection points |
| Primary Limitations | Vulnerable to water spread along cable length | Not ideal for environments with constant side moisture |
| Cost Effectiveness | Often more affordable for outdoor setups | Higher cost for critical entry-point protection |
Different industries require specific cable features to maintain operational efficiency and avoid costly interruptions due to water ingress.
Recommendation: Longitudinally Waterproof Cables
Reason: Protects sensitive data lines and connections from moisture spread, minimizing downtime.
Recommendation: Laterally Waterproof Cables
Reason: Suitable for outdoor setups or areas where moisture might impact cable sides but not specific connection points.
Recommendation: Laterally Waterproof Cables
Reason: Ideal for use in subterranean tunnels and conduits where environmental moisture is the primary concern.
Waterproof cables, whether laterally or longitudinally waterproof, represent an essential technological solution to prevent water ingress and protect critical infrastructure. By understanding the unique properties and applications of each, engineers and facility managers can make informed choices tailored to their specific environmental needs.
Investing in the right waterproof cable not only enhances the reliability of systems but also contributes to the long-term durability of infrastructure, making a noticeable difference in overall performance and cost-effectiveness.
Whether your setup demands protection from side water ingress or water spread along the cable's length, choosing the right cable can ensure your systems remain safe, efficient, and operational, even in the harshest conditions.